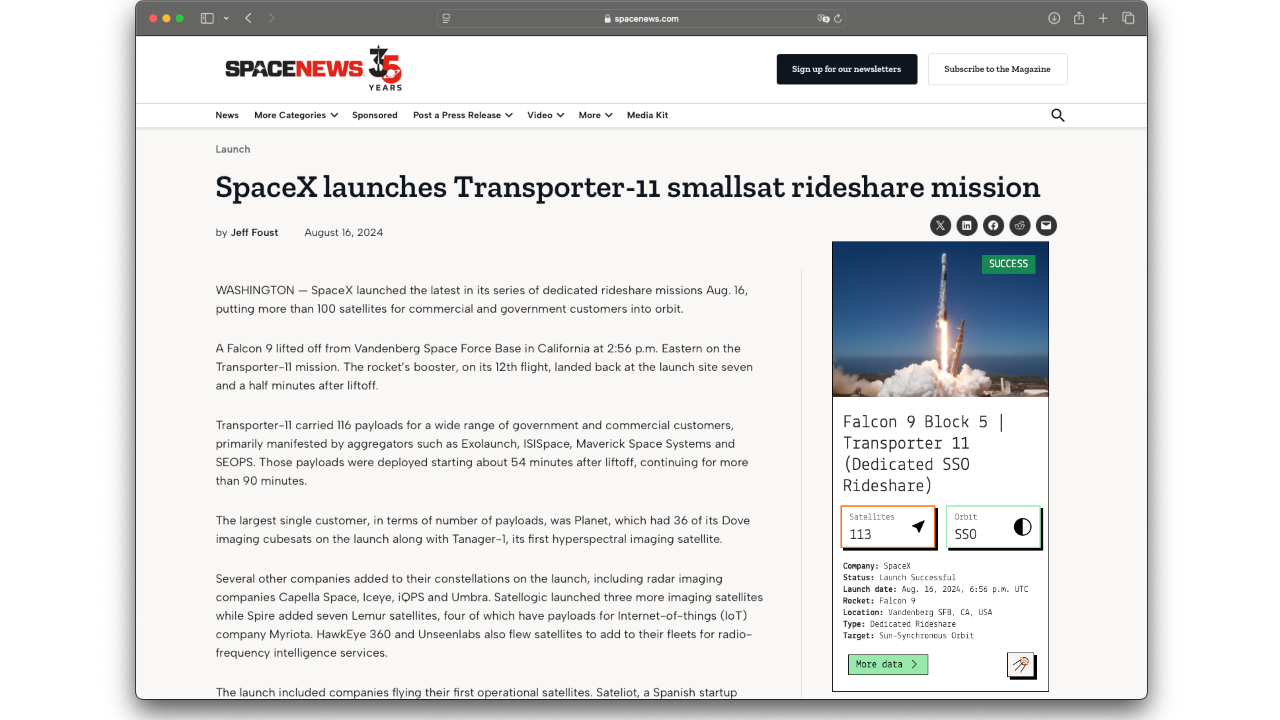
Key statistics
Satellite ALOS at a glance.
Uptime
7264
Days in orbit
Revolutions
≈ 14.7
Per day
Orbit
SSO
Sun Synchronous Orbit
Inclination
98.1
Latest
Satellite identification and parameters
Extended collection of information and parameters for ALOS.
Object identification
Identified? True
Debris? False
Object name: ALOS
International designator: 2006-002A
Object number (NORAD): 28931
Object ID (CCSDS): 28931
Country: JAPAN (JPN)
Current information (Y/N): Y
RCS size: LARGE
Orbital parameters
Period: 97.993 minutes
Inclination: 98.1091 deg
SMA: 7040.846 km
Apoapsis: 663.5 km
Periapsis: 661.922 km
RAAN: 297.7774 deg
Eccentricy: 0.00011206
Argument of periapsis: 115.826 deg
Mean anomaly: 244.3061 deg
Mean motion: 14.69486288 rev/day
Mean motion (dot): 0.00002463 rev/day2
B* drag term: 0.00042383716 1/REarth
Two-line elements (TLE)
Creation date: Dec. 12, 2025, 10:14 a.m.
Reference frame: TEME
Reference center: EARTH
Epoch: Dec. 12, 2025, 6:53 a.m. UTC
TLE line 0: 0 ALOS
TLE line 1: 1 28931U 06002A 25346.28687871 .00002463 00000-0 42384-3 0 9997
TLE line 2: 2 28931 98.1091 297.7774 0001121 115.8260 244.3061 14.69486288 60646
Live tracking on map
Real-time ground track for satellite ALOS.
In-orbit conjunctions
A list of the most updated potential collisions computed for object ALOS.
Associated space launch
ALOS (Advanced Land Observation Satellite) is used for cartography, regional observation, disaster monitoring, and resource surveying. ALOS has three remote-sensing instruments: - the Panchromatic Remote-sensing Instrument for Stereo Mapping (PRISM) for digital elevation mapping with 2.5 meter resolution, - the Advanced Visible and Near Infrared Radiometer type 2 (AVNIR-2) for precise land coverage observation with 10 meter resolution, and - the Phased Array type L-band Synthetic Aperture Radar (PALSAR) for day-and-night and all-weather land observation. ALOS transmitts its data via the DRTS (Kodama) satellite. The ALOS was launched by an H-2A-2022 launch vehicle from the Tanegashima Space Center. ALOS as been given the nickname Daichi. Five minutes after spacecraft separation, ALOS began to unfurl its 72-foot solar array that will provide electrical power to the craft throughout its mission. Six cameras are on-board to visually verify the correct deployment of the solar panel and various instrument antennas. ALOS lost all power on 22. April 2011, thus ending the mission.
ALOS was lifted into orbit during the mission ‘H-IIA 2022 | Daichi’, on board a H-IIA 2022 space rocket.
The launch took place on Jan. 24, 2006, 1:33 a.m. from Yoshinobu Launch Complex LP-1.
For more information about the launch, click the button.
H-IIA 2022 | Daichi
Agency: N/A
Status: Launch Successful
Launch date: Jan. 24, 2006, 1:33 a.m. UTC
Rocket: H-IIA 2022
Launch pad: Yoshinobu Launch Complex LP-1
Location: Tanegashima Space Center, Japan
...
Latest news about this satellite
There are no fresh news available about this satellite. Check back as we update our databases every day.
Newsletter sign-up
Weekly statistics, charts and insights to help you stay on top of the space industry.