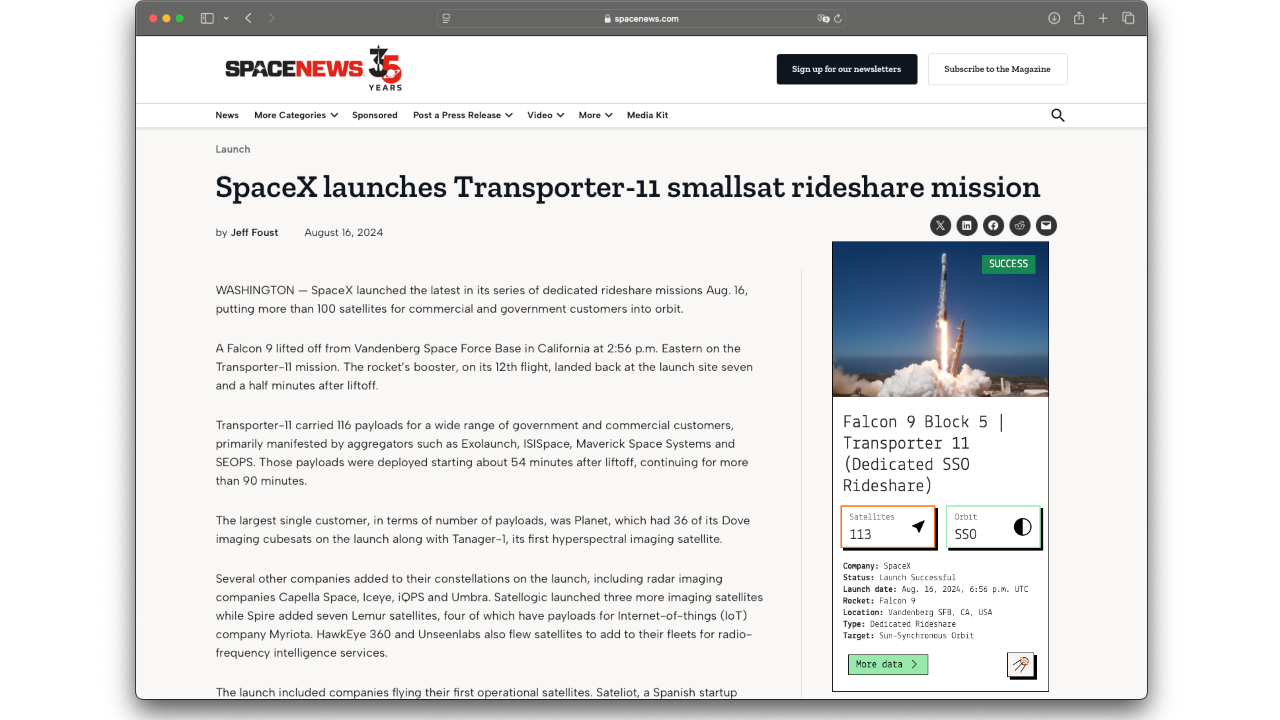
Key statistics
Satellite GCOM-C at a glance.
Uptime
2818
Days in orbit
Revolutions
≈ 14.3
Per day
Orbit
SSO
Sun Synchronous Orbit
Inclination
98.7
Latest
Satellite identification and parameters
Extended collection of information and parameters for GCOM-C.
Object identification
Identified? True
Debris? False
Object name: GCOM-C
International designator: 2017-082A
Object number (NORAD): 43065
Object ID (CCSDS): 43065
Country: JAPAN (JPN)
Current information (Y/N): Y
RCS size: LARGE
Orbital parameters
Period: 100.893 minutes
Inclination: 98.6605 deg
SMA: 7179.053 km
Apoapsis: 801.58 km
Periapsis: 800.257 km
RAAN: 324.0022 deg
Eccentricy: 0.00009215
Argument of periapsis: 91.2936 deg
Mean anomaly: 268.835 deg
Mean motion: 14.2725647 rev/day
Mean motion (dot): 0.00000147 rev/day2
B* drag term: 0.000078148929 1/REarth
Two-line elements (TLE)
Creation date: Sept. 9, 2025, 10:35 a.m.
Reference frame: TEME
Reference center: EARTH
Epoch: Sept. 9, 2025, 2:27 a.m. UTC
TLE line 0: 0 GCOM-C
TLE line 1: 1 43065U 17082A 25252.10244989 .00000147 00000-0 78149-4 0 9994
TLE line 2: 2 43065 98.6605 324.0022 0000921 91.2936 268.8350 14.27256470401846
Live tracking on map
Real-time ground track for satellite GCOM-C.
In-orbit conjunctions
There are no conjunctions computed for GCOM-C, at the moment. Check back to stay up to date, as we update our databases every day.
Go to all conjunctionsAssociated space launch
GCOM-C1 is another satellite in JAXA's Earth observation Global Change Observation Mission (GCOM) constellation. This spacecraft is the first satellite in GCOM-C series and is intended to operate in sun-synchronous orbit for 5 years. It aims to collect surface and atmospheric measurements in order to monitor global climate change. Along with it is launched an engineering test satellite SLATS (Super Low Altitude Test Satellite), which is an attempt to develop techniques to operate a satellite in extremely low orbits. SLATS will try achieve that by maintaining position in orbit via ion engines. It will also collect data on atmosphere density and measure atomic oxygen in such low altitudes.
GCOM-C was lifted into orbit during the mission ‘H-IIA 202 | GCOM-C1 & SLATS’, on board a H-IIA space rocket.
The launch took place on Dec. 23, 2017, 1:26 a.m. from Yoshinobu Launch Complex LP-1.
For more information about the launch, click the button.
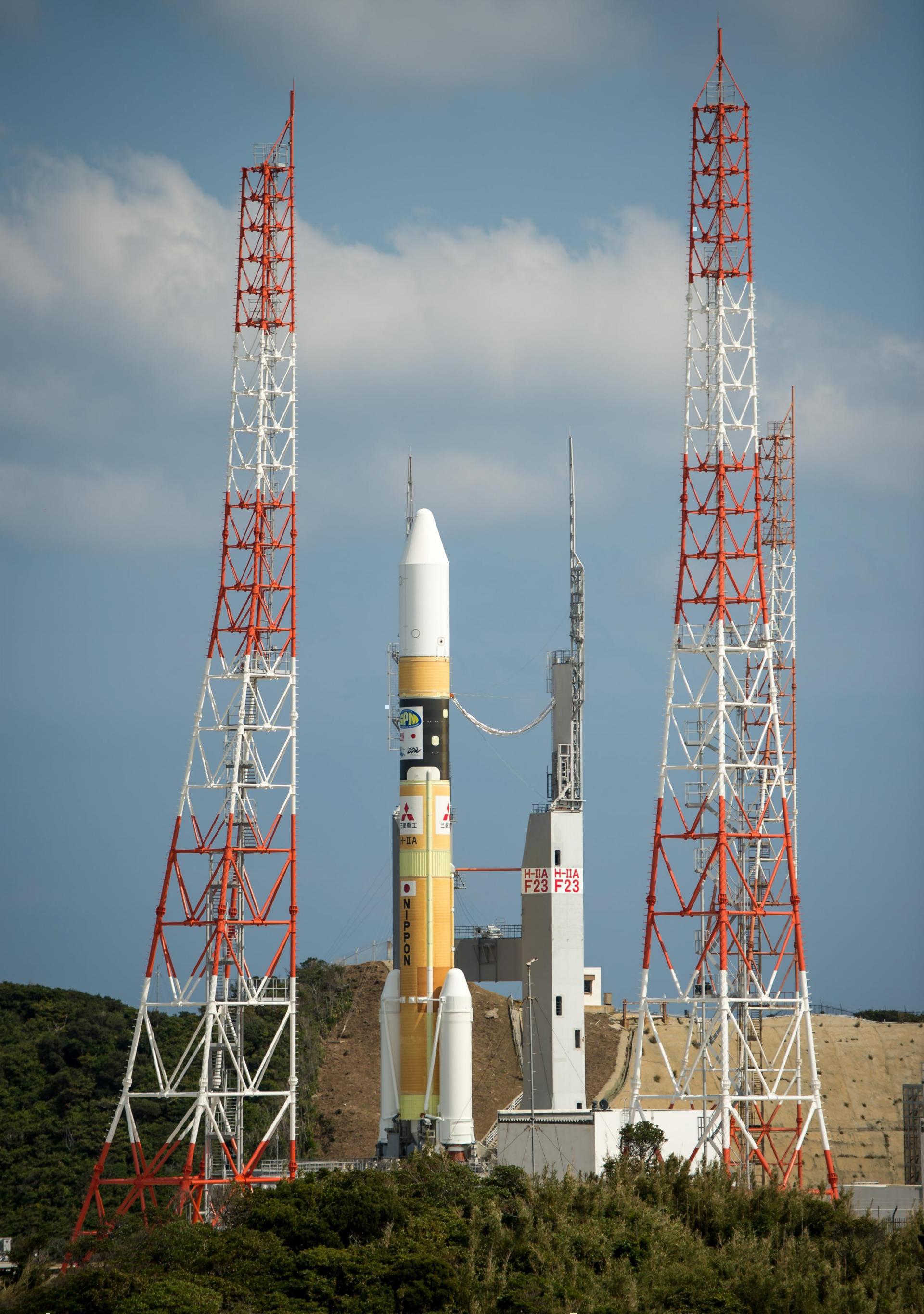

H-IIA 202 | GCOM-C1 & SLATS
Agency: N/A
Status: Launch Successful
Launch date: Dec. 23, 2017, 1:26 a.m. UTC
Rocket: H-IIA
Launch pad: Yoshinobu Launch Complex LP-1
Location: Tanegashima Space Center, Japan
...
Latest news about this satellite
There are no fresh news available about this satellite. Check back as we update our databases every day.
Newsletter sign-up
Weekly statistics, charts and insights to help you stay on top of the space industry.