Key statistics
Satellite ASO-S at a glance.
Uptime
1164
Days in orbit
Revolutions
≈ 14.5
Per day
Orbit
SSO
Sun Synchronous Orbit
Inclination
98.3
Latest
Satellite identification and parameters
Extended collection of information and parameters for ASO-S.
Object identification
Identified? True
Debris? False
Object name: ASO-S
International designator: 2022-129A
Object number (NORAD): 54029
Object ID (CCSDS): 54029
Country: PEOPLES REPUBLIC OF CHINA (PRC)
Current information (Y/N): Y
RCS size: LARGE
Orbital parameters
Period: 99.176 minutes
Inclination: 98.2749 deg
SMA: 7097.396 km
Apoapsis: 728.737 km
Periapsis: 709.785 km
RAAN: 350.4376 deg
Eccentricy: 0.00133515
Argument of periapsis: 305.7754 deg
Mean anomaly: 54.22 deg
Mean motion: 14.51958403 rev/day
Mean motion (dot): 0.00000344 rev/day2
B* drag term: 0.000096115609 1/REarth
Two-line elements (TLE)
Creation date: Dec. 14, 2025, 3:07 a.m.
Reference frame: TEME
Reference center: EARTH
Epoch: Dec. 13, 2025, 4:16 p.m. UTC
TLE line 0: 0 ASO-S
TLE line 1: 1 54029U 22129A 25347.67811613 .00000344 00000-0 96116-4 0 9998
TLE line 2: 2 54029 98.2749 350.4376 0013352 305.7754 54.2200 14.51958403168507
Live tracking on map
Real-time ground track for satellite ASO-S.
In-orbit conjunctions
There are no conjunctions computed for ASO-S, at the moment. Check back to stay up to date, as we update our databases every day.
Go to all conjunctionsAssociated space launch
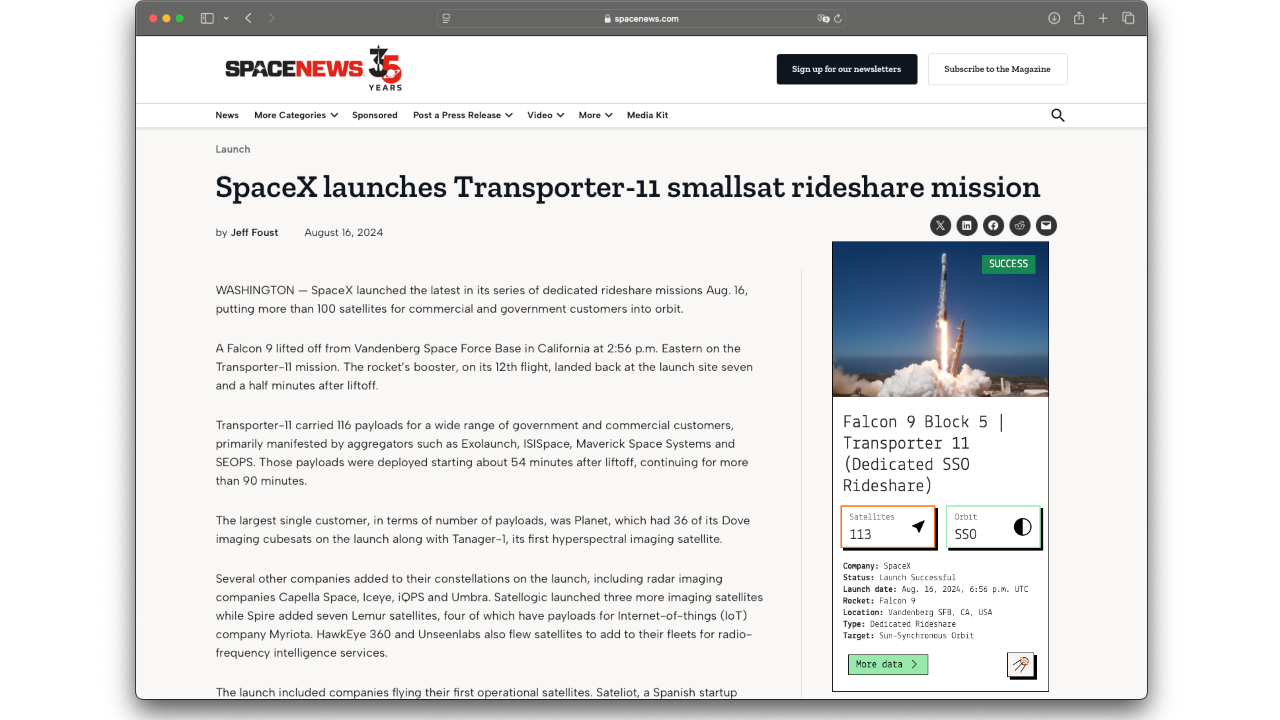
ASO-S (Advanced Space-borne Solar Observatory) is a Chinese solar space observatory that aims to study the interaction between the Sun's magnetic field, solar flares and coronal mass ejections. It's the first space solar observatory of China. ASO-S is a 3-axis stabilized satellite with a mass of less than 1,000 kg with a pointing accuracy of 0.01° and an orientation stability of 1 to 2 arc seconds every 20 seconds. The payload has a mass below 335 kg and consumes about 300 watts. The platform's pointing accuracy is lower than 0.01°, the measurement accuracy is lower than 1 arc second and the orientation drift is below 0.0004°/s. ASO-S has three instruments: - The Full-Disc Vector Magnetograph (FMG) instrument is intended to map the magnetic field of the photosphere over the entire solar disk. It includes an imager, an optical polarization system and a CCD detector. - The Hard X-ray Imager (HXI) camera should image the whole solar disk in X-rays. The instrument is optimized to take images of solar flares. - A set of three LST (Lyman-alpha Solar Telescope) telescopes is used to observe the Lyman-alpha line (121.6 nm) of solar flares up to a distance of several solar radii from the Sun's disk. These three telescopes are SDI (to obtain an image of the solar disk), SCI (coronagraph for observation between 1.1 and 2.5 solar radii) and WST (white light emitted by the solar disk used for calibration purposes).
ASO-S was lifted into orbit during the mission ‘Long March 2D | Advanced Space-borne Solar Observatory (ASO-S)’, on board a Long March 2D space rocket.
The launch took place on Oct. 8, 2022, 11:43 p.m. from Launch Area 94 (SLS-2 / 603).
For more information about the launch, click the button.
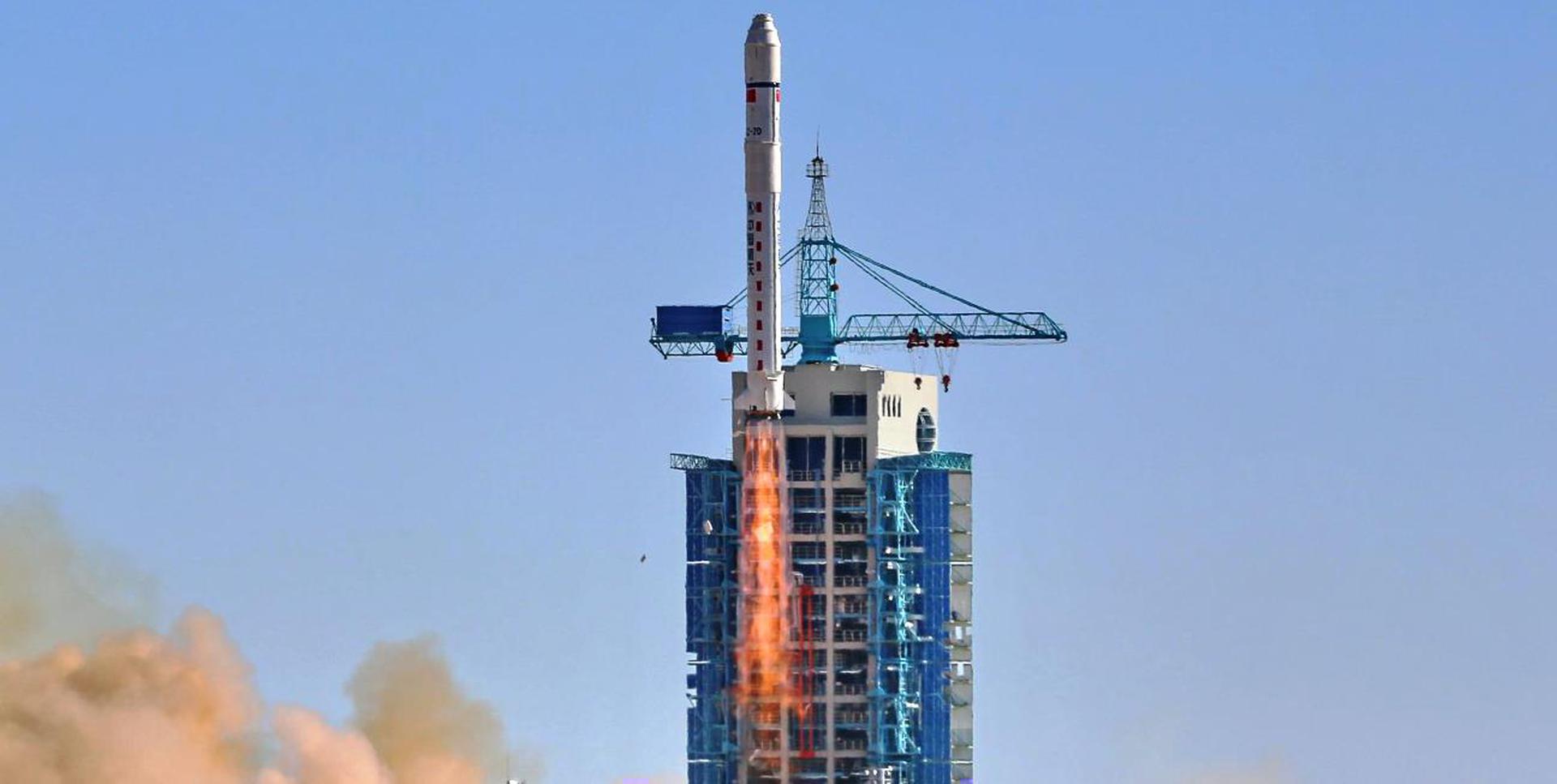

Long March 2D | Advanced Space-borne Solar Observatory (ASO-S)
Agency: N/A
Status: Launch Successful
Launch date: Oct. 8, 2022, 11:43 p.m. UTC
Rocket: Long March 2D
Launch pad: Launch Area 94 (SLS-2 / 603)
Location: Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center, People's Republic of China
...
Latest news about this satellite
There are no fresh news available about this satellite. Check back as we update our databases every day.
Newsletter sign-up
Weekly statistics, charts and insights to help you stay on top of the space industry.